Sensitive Data Configuration in aspnet core
When starting a new project on ASP.NET CORE, there comes a point where we need to start storing sensitive configuration data.
OAuth keys, Client Ids, Client Secrets and other confidential data’s which are need to be stored safely. Depending on your context you may not want to be storing these types of application settings in configuration files that are committed to source control.
Local environment for development and once the project is deployed to Azure have completely different configurations.
So we need to change from local to production. Let us see how?
If you have been using appsettings from the app.config and web.config, there are transforming and replacing values with tools like SlowCheetah or through Octopus Deploy.
With ASP.NET Configurations, there’s a new way to do this.
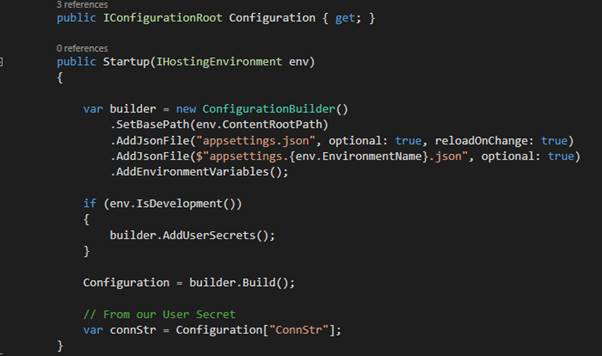
Configuration
ASP.NET Core has a ConfigurationBuilder that enables you to load application settings from various places. If you’ve loaded up a brand new ASP.NET Core app, you’re Startup looks something like this:
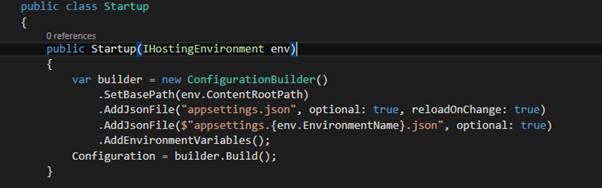
Asp.Net core provides a new appsettings.json file for us to use as well as an optional appsettings for each different environment.
For local development, you can use appsetting.json however for the security You want to keep your sensitive data out of this file.
For this, User Secrets is an great option to use.
User Secrets
ASP.NET Core adds a new way to store your sensitive data with User Secrets.
User Secrets are simply a plain text json file that are stored in your systems user profile directory. This means the file is storred ouside of your project directory.
There are a couple ways to manage your user secrets:
- At first, Add Microsoft.Extensions.Secret Manage.Tools in the tools section of your project.json.
- If you are using the dotnet CLI then you should be able to run dotnet user-secrets versions
- Next in your project.json you want to add a ”userSecretsId” property in the root. The value can be anything you want but it should be unique so it does not collide with another user secrets you create for any other project.
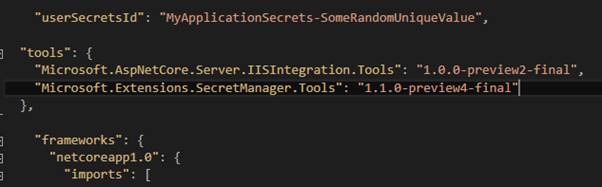
In order to load the secrets file, you need to first add Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.UserSecrets package in your project.json
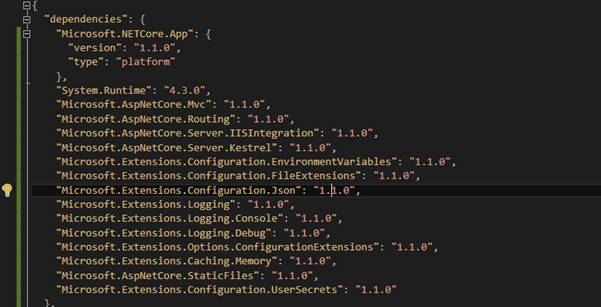
Since user secrets are used only for local development, we can now load the secrets using the ConfigurationBuilder in our Startup.
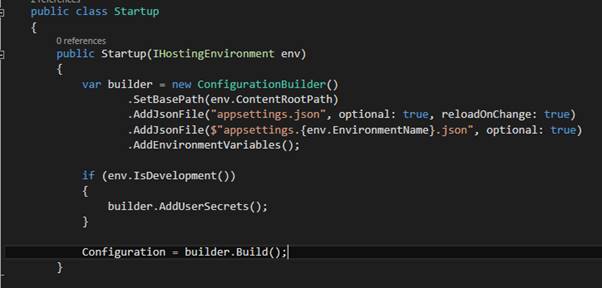
Visual Studio
If you are using Visual Studio, you can edit your user secrets file by accessing it in the context menu of your project in the solution explorer.
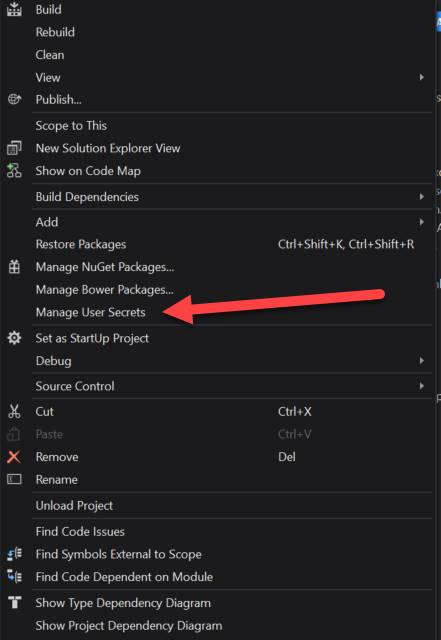
CLI
If you are using the dotnet CLI then you can call dotnet user-secrets [options] [command] to clear, list, remove and set secrets.
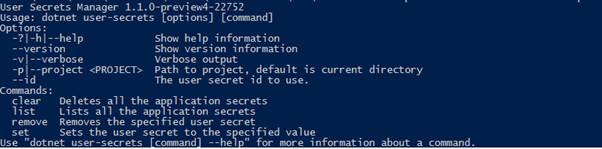
Example
Simple example would be wanting to store the connection string to a database.
dotnet user-secrets set ConnStr "User ID=Derek;Password=CodeOpinion;"
Now within our code we can access the connection string after we built our configuration from the ConfigurationBuilder.