Response Caching in ASP.Net Core
Problem:
How to cache responses in ASP.NET Core?
Solution:
To use this middleware, make sure you have ASP.NET Core installed. You can download and install the .NET Core SDK from here.
Let’s create an ASP.NET Core application. Open Project.json and include following nugget package.Once the package is restored, now we need to configure it. So open Startup.cs, add highlight line of code in configureservices method.
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.ResponseCaching":"2.0.0",
Once the package is restored, now we need to configure it. So open Startup.cs, add highlight line of code in configureservices method.
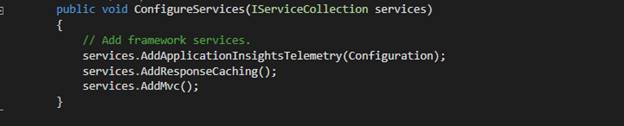
And now let’s add this middleware to HTTP pipeline, so add highlighted line in the configure method of Startup.cs
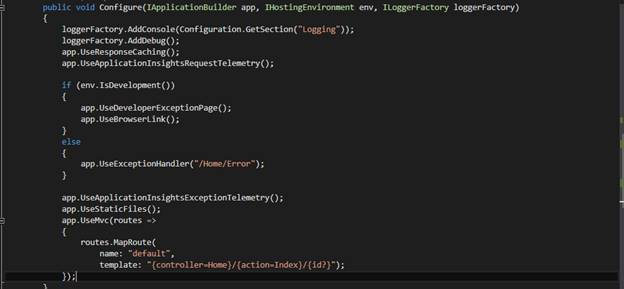
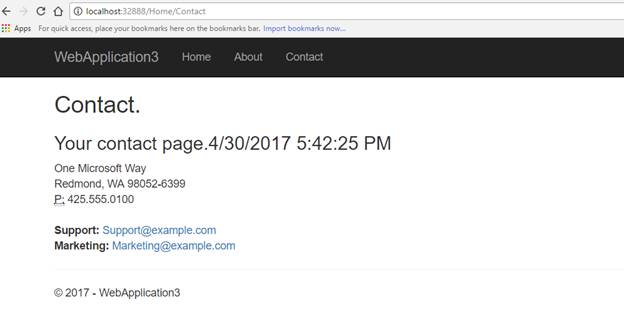
We are done with all configurations. To use it, you need to include responseCache attribute on controller’s action method. So open HomeController.cs and add responseCache attribute to Contact method and set the duration to 20 seconds. For the demo, I modified the contact method and add Date time to see response caching in action.
![]()
Here the cache location is public and expiration is set to 20 seconds. Read this article to know more about HTTP Caching.
Now let’s run the application to see it in action. When you visit contact page, you should see the current date and time of your system. As the cache duration is set to 20 seconds, the response will be cached for 20 seconds. You can verify it via visiting other pages of the application and then coming back to Contact page.

During a browser session, browsing multiple pages within the website or using back and forward button to visit the pages, content will be served from the local browser cache (if not expired). But when the page refresh the request will be go to the server and page content will get refreshed. You can verify it via refreshing contact page using F5. So when you hit F5, response caching expiration value has no role to play to serve the content. You should see 200 response for contact request.
Static contents (like image, css, js) when refreshed, will result in 300 not modified. if nothing has changed for the requested content. This is due to the Etag last Modified and value append in the response header. See below image (Screenshot taken in Firefox).

When a resource is requested from the site, the browser sends Etag and last-modified value in the request header as if not match and if modified sence . The server compares this header’s value against the value present on the server. If values are same, then server doesn’t send the content again. Instead, the server will send a 304 not modified response, and this tells the browser to use previously cached content.
