SQL Server Stored Procedures: Part-4

SQL Server TRY CATCH
For SQL Server Stored Procedures: Part-3, Click here.
TRY CATCH Statement
SQL Server TRY CATCH construct is used to handle error in stored procedure.
Syntax:
BEGIN TRY
--Statements that may cause exceptions
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
--Statements that handle exceptions
END CATCH
If TRY block executes without any error then CATCH block does not executes. But if TRY block executes with error then control transfers to the statements in CATCH block.
Functions of CATCH Block:
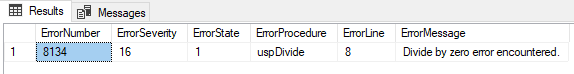
- ERROR_LINE() gives the line number on which exception occurred
- ERROR_MESSAGE() gives complete text of generated error message
- ERROR_PROCEDURE() gives stored procedure name where error occurred
- ERROR _NUMBER() gives number of error occurred
- ERROR_SEVERITY() gives severity level of the error occurred
- ERROR_STATE() gives state number of error occurred
Example of TRY CATCH:
ALTER PROC uspDivide(
@x AS DECIMAL,
@y AS DECIMAL,
@z AS DECIMAL OUTPUT
) AS
BEGIN
BEGIN TRY
SET @z = @x / @y;
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
SELECT
ERROR_NUMBER() AS ErrorNumber
,ERROR_SEVERITY() AS ErrorSeverity
,ERROR_STATE() AS ErrorState
,ERROR_PROCEDURE() AS ErrorProcedure
,ERROR_LINE() AS ErrorLine
,ERROR_MESSAGE() AS ErrorMessage
END CATCH
END
Calling stored procedure giving values:
DECLARE @a AS DECIMAL;
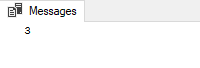
EXEC uspDivide 6, 2, @a OUTPUT;
PRINT @a;
Output:
Dividing 6/0:
DECLARE @a AS DECIMAL;
EXEC uspDivide 6, 0, @a OUTPUT;
PRINT @a;
Output:
TRY CATCH with transactions:
Test the state of transactions we can use XACT_STATE() function inside a CATCH block.
- If XACT_STATE() function returns -1, that means uncommittable transaction is pending then ROLLBACK TRANSACTION statement should be issued.
- If XACT_STATE() function returns 1, that means committable transaction is pending then COMMIT TRANSACTION statement should be issued.
- if XACT_STATE() function returns 0, that means no transaction is pending and no need to take any action.
To ensure consistency in CATCH block, you can use transaction state before issuing COMMIT or ROLLBACK TRANSACTION.
For example:
Sample tables:
CREATE TABLE dbo.students
(
studentId INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY,
firstName VARCHAR(60),
lastName VARCHAR(60)
)
CREATE TABLE dbo.course
(
courseId INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY,
studentId INT NOT NULL,
infoStu VARCHAR(100),
FOREIGN KEY(studentId) REFERENCES dbo.students(studentId)
)
INSERT INTO dbo.students(firstName,lastName) VALUES ('jack','Sparrow'),('Ram', 'Sparrow')
INSERT INTO dbo.course(studentId, infoStu) VALUES(1,'He is a Good Boy')
Create new procedure to be used in CATCH block maned uspReportError
CREATE PROCEDURE uspReportError
AS
SELECT
ERROR_NUMBER() AS ErrorNumber
,ERROR_SEVERITY() AS ErrorSeverity
,ERROR_STATE() AS ErrorState
,ERROR_PROCEDURE() AS ErrorProcedure
,ERROR_LINE() AS ErrorLine
,ERROR_MESSAGE() AS ErrorMessage
Now create procedure to delete a row form the dbo.students table:
CREATE PROCEDURE uspDeleteStudent(@studentId INT)
AS
BEGIN
BEGIN TRY
BEGIN TRANSACTION
DELETE FROM dbo.students
WHERE studentId = @studentId
COMMIT TRANSACTION
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
EXEC uspReportError
IF(XACT_STATE())=-1
BEGIN
PRINT 'Transaction is in umcommitable state. start ROLLBACK TRANSACTION'
ROLLBACK TRANSACTION
END
IF(XACT_STATE())=1
BEGIN
PRINT 'Transaction is in commitable state. start COMMIT TRANSACTION'
COMMIT TRANSACTION
END
END CATCH
END
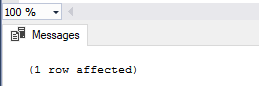
Call stored procedure uspDeleteStudent to delete studentId 2:
EXEC uspDeleteStudent 2;
Output:
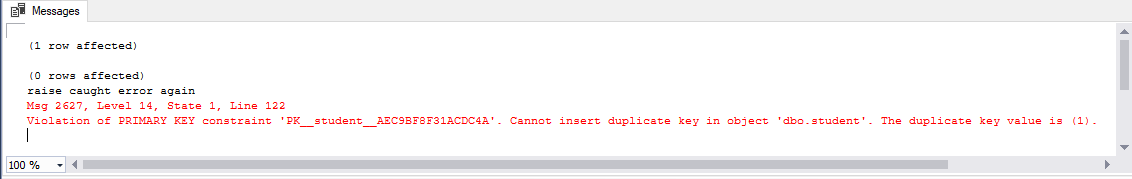
Finally Call stored procedure uspDeleteStudent to delete studentID 1:
EXEC uspDeleteStudent 1;
Output:
THROW statement:
THROW statement is used to raise an exception and transfer execution to the CATCH Block of TRY CATCH statement in SQL Server.
Syntax:
THROW [error_number, message, state]
Syntax description:
- error_number is a integer type and must be greater than 50000 and less than or equal to 2,147,483,647.
- message is string type NVARCHAR(2048) which describes exception.
- state is a TINYINT with value 0-255, which indicates state associated with message.
We should place THROW statement in CATCH block if we don’t have any parameter for THROW statement.
For Examples:
To raise an Exception:
Use THROW statement to raise exception:
THROW 50006, N'An error occurred', 5;
Output:
Msg 50006, Level 16, State 5, Line 112
An error occurred
To rethrow Exception:
Sample table student:
CREATE TABLE student(
stuId int primary key
)
Use THROW statement without argument in CATCH block to rethrow CATCH error
BEGIN TRY
INSERT INTO student(stuId) VALUES(1)
INSERT INTO student(stuId) VALUES(1)
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
PRINT('raise caught error again');
THROW;
END CATCH
Output:
For SQL Server Stored Procedure: Part-5, Click here.