Use of TOP and DISTINCT in SQL SERVER
TOP and DISTINCT clause.

TOP applies to: SQL Server (starting with 2008), Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Data Warehouse and Parallel Data Warehouse
DISTINT applies to: SQL Server Analysis Services
TOP Clause:
TOP is mainly used to limit the result of query in terms of number or percentage of the result from database. It selects result limits to TOP from N numbers of data from ordered rows by using ORDER BY statement otherwise it selects undefined order data. TOP can be used in statements SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, INSERT, or MERGE statement.
To predict the rows affected can be indicated by using ORDER BY clause with TOP clause which is one of the best practice using TOP clause.
Note: If you don't have database to test then see my previous article. Click here.
Syntax:
SELECT TOP <expression> [PERCENT]
[WITH TIES]
FROM
<table_name>
ORDER BY
<column_name>
Syntax description:
You can use clauses like WHERE, JOIN, HAVING and GROUP BY with SELECT statement.
<expression>
It specifies the number of rows to be returned. <expression> is in float value if [PERCENT] is used otherwise it is in BIGINT.
[PERCENT]
[PERCENT] keyword is used to give N percentage of rows result.
[WITH TIES]
This keyword is used to return addition value that matches limited last result.
Examples of SELECT TOP statement:
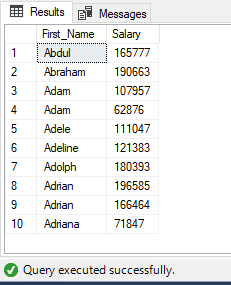
Using TOP in constant value:
Constant value to return the top 10.
SELECT TOP 10
First_Name,
Salary
FROM
EmployeeDb
ORDER BY
First_Name,Salary DESC
Output:
TOP to return PERCENT of ROWS
Returns percent of total results of rows:
SELECT TOP 1 PERCENT
First_Name,
Salary
FROM
EmployeeDb
ORDER BY
First_Name DESC
Output:
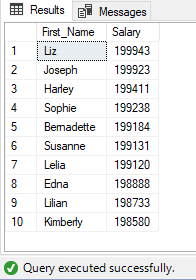
Using TOP WITH TIES
Returns top 3 first name:
SELECT TOP 3 WITH TIES
First_Name,
Salary
FROM
EmployeeDb
ORDER BY
First_Name
Output:
Output returns four value, fourth is returned WITH TIES as it is similar to third value.
DISTINCT clause
It selects only different value which eliminates duplicate record form the result. It only operates on single column and can be used in COUNT, AVG, MAX, etc. while using DISTINCT on column with multiple NULL values, it returns only one NULL as it treats multiple NULL as one distinct value. DINSTINT cannot be operated on multiple column.
In single column:
Syntax:
SELECT DINTINCT
<column_name>
FROM
<table_name>
It returns distinct values from the specified column.
Examples of DISTINCT clause:
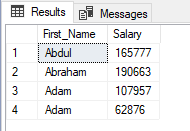
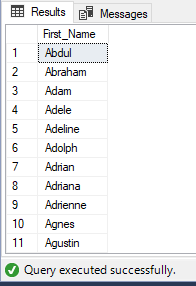
Without using DISTINCT:
SELECT
First_Name
FROM
EmployeeDb
ORDER BY
First_Name
Output:
Output have duplicate first names.
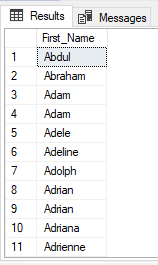
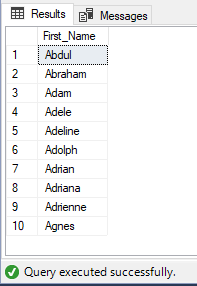
Using DISTINCT:
SELECT DISTINCT
First_Name
FROM
EmployeeDb
ORDER BY
First_Name
Output:
Duplicates were removed form column.
Use of DISTINCT and TOP
Implementation of DISTINCT and TOP in a column. It also cannot be operated on multiple columns.
Example:
SELECT DISTINCT TOP 10
First_Name
FROM
EmployeeDb
ORDER BY
First_Name
Output: