SQL Server Stored Procedures: Part-1

If you don't have database, you can find it here.
Creating Stored Procedure:
CREATE PROCEDURE or CREATE PROC query is used to create stored procedure:
CREATE PROCEDURE uspEmployeeList
AS
BEGIN
SELECT
Emp_ID,
First_Name,
Last_Name
FROM
dbo.EmployeeDb
ORDER BY
Emp_ID
END
Syntax Description:
- uspEmployeeList is the name of the stored procedure.
- AS keyword seperates the head and body of stored procedure.
- BEGIN and END keywords surrounding statement are optional in case of one statement in stored procedure.
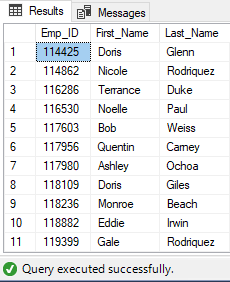
Ouput (After Execution):
Commands completed successfully.
Executing a Stored Procedure:
EXECUTE or EXEC statement is followed by stored procedure name.
EXECUTE uspEmployeeList
Output:
Modifying Stored Procedure:
ALTER is used instead of CREATE for modifying existing Procedure.
ALTER PROCEDURE uspEmployeeList
AS
BEGIN
SELECT
Emp_ID,
First_Name,
Last_Name
FROM
dbo.EmployeeDb
ORDER BY
First_Name
END
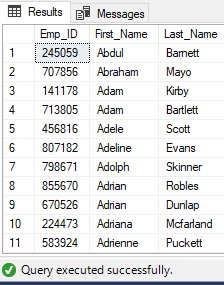
Ouput (After Execution):
Commands completed successfully.
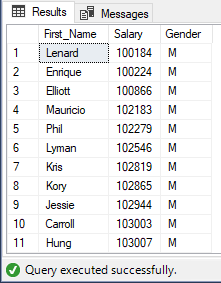
Execute Stored Procedure to view changes:
EXEC uspEmployeeList
Partial Output:
Deleting Stored Procedure:
DROP PROCEDURE or DROP PROC statement is used to delete Stored Procedure.
DROP PROCEDURE uspEmployeeList
Stored Procedure with one parameter:
First, you can create stored procedure:
CREATE PROCEDURE uspEmployeeSalary
AS
BEGIN
SELECT
First_Name,
Last_Name,
Salary
FROM
dbo.EmployeeDb
ORDER BY
First_Name
END
We can add parameter to the stored procedure to find name whose salary are greater than input price:
ALTER PROCEDURE uspEmployeeSalary(@minSalary AS DECIMAL)
AS
BEGIN
SELECT
First_Name,
Last_Name,
Salary
FROM
dbo.EmployeeDb
WHERE
Salary >= @minSalary
ORDER BY
Salary
END
Syntax Description:
- @minSalary parameter is added to stored procedure uspEmployeeSalary .
- @ sign must be used for every parameter.
- AS DECIMAL keywords specify data typeof parameter @minSalary
- @minSalary parameter is used in WHERE clause of the SELECT statement
Ouput (After Execution):
Commands completed successfully.
Executing a stored procedure with one parameter:
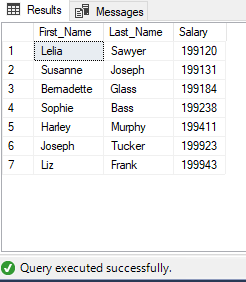
We need to pass an argument to stored procedure as:
EXEC uspEmployeeSalary 199000
Output:
Stored Procedure with multiple parameters:
Stored procedure also takes string parameters. The parameters are separated by commas. The Following statement modifies uspEmployeeSalary by adding @maxSalary and @gender parameters.
ALTER PROCEDURE uspEmployeeSalary(@minSalary AS DECIMAL, @maxSalary AS DECIMAL,@gender AS VARCHAR(1))
AS
BEGIN
SELECT
First_Name,
Salary,
Gender
FROM
dbo.EmployeeDb
WHERE
Salary >= @minSalary AND
Salary <= @maxSalary AND
Gender LIKE '%' +@gender+ '%'
ORDER BY
Salary
END
In WHERE clause of SELECT statement we can add following condition for text parameter:
Gender LIKE '%' +@gender+ '%'
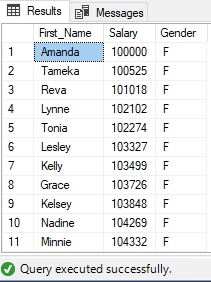
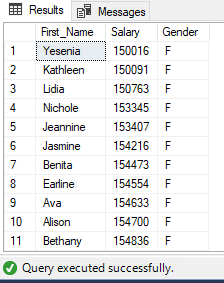
After modification of stored procedure we can execute it as:
EXEC uspEmployeeSalary @minSalary=100000, @maxSalary=200000,@gender='F';
Partial Output:
Optional Patameters:
We must pass all three arguments corresponding to three parameters while executing uspEmployeeSalary stored procedure.
In SQL Server, we can specify default valure for parameters to skip the parameters with default values.
It can be done as follows:
ALTER PROCEDURE uspEmployeeSalary(
@minSalary AS DECIMAL=100000,
@maxSalary AS DECIMAL=200000,
@gender AS VARCHAR(1))
AS
BEGIN
SELECT
First_Name,
Salary,
Gender
FROM
dbo.EmployeeDb
WHERE
Salary >= @minSalary AND
Salary <= @maxSalary AND
Gender LIKE '%' +@gender+ '%'
ORDER BY
Salary
END
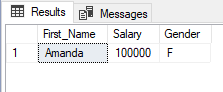
After compiling stored procedure, we can execute stored procedure without passing arguments to @minSalary and @maxSalary parameters as:
EXEC uspEmployeeSalary @gender='M';
Partial Output:
Passing NULL value as default value:
Stored procedure using NULL value of parameter is given as:
ALTER PROCEDURE uspEmployeeSalary(
@minSalary AS DECIMAL=100000,
@maxSalary AS DECIMAL=NULL,
@gender AS VARCHAR(1))
AS
BEGIN
SELECT
First_Name,
Salary,
Gender
FROM
dbo.EmployeeDb
WHERE
Salary >= @minSalary AND
(Salary IS NULL OR Salary <= @maxSalary) AND
Gender LIKE '%' +@gender+ '%'
ORDER BY
Salary
END
To handle NULL value for parameter we have used following in WHERE clause:
(Salary IS NULL OR Salary <= @maxSalary)
Statement for executing stored procedure:
EXEC uspEmployeeSalary
@minSalary=150000,
@gender='F'
Partial Output:
Declaring variable:
DECLARE statement is used for declaring variable followed by variable name as @gender and data type of variable:
DECLARE @salary INT, @gender VARCHAR
Assigning value to a variable:
SET statement is used for assigning value to variable.
SET @salary=100000
SET @gender='F'
Using variable in a query:
SELECT statement uses the @gender variable in WHERE clause to find the gender of employee:
SELECT
First_Name,
Salary,
Gender
FROM
dbo.EmployeeDb
WHERE
Salary=@salary AND
Gender=@gender
ORDER BY
Salary
Combining all statement we can execute code block as:
DECLARE
@salary INT, @gender VARCHAR
SET @salary=100000
SET @gender='F'
SELECT
First_Name,
Salary,
Gender
FROM
dbo.EmployeeDb
WHERE
Salary=@salary AND
Gender=@gender
ORDER BY
Salary
Output:
Storing query result in variable:
DECLARE @employeeCount INT;
SET @employeeCount = (
SELECT
COUNT(*)
FROM
dbo.EmployeeDb
)
SELECT @employeeCount;
Output of the content of the storing variable can be printed as:
SELECT @EmployeeCount
Or
PRINT @EmployeeCount
Or
PRINT ‘The Number of Employee is’ +CAST(@EmployeeCount AS VARCHAR(MAX));
Output:
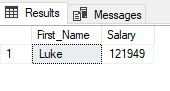
Selecting a record into variables:
Code block for selecting record into variables :
DECLARE
@employeeName VARCHAR(MAX),
@salary INT
SELECT
@employeeName=First_Name,
@salary=Salary
FROM
dbo.EmployeeDb
WHERE
Gender='M'
SELECT
@employeeName AS First_Name,
@salary AS Salary
Output:
Accumulating values into variables:
ALTER PROCEDURE uspEmployeeList(@gender VARCHAR)
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @employeeList VARCHAR(MAX)
SET @employeeList=''
SELECT
@employeeList=@employeeList+ First_Name+CHAR(10)
FROM
dbo.EmployeeDb
WHERE
Gender=@gender
ORDER BY
First_Name
PRINT
@employeeList
END
Syntax Description:
- At first, declare a variable named @employeeList with varying character string type and set its value blank.
- Next, select the employee name list form the employee table based on the input of @gender. In this list, we store the employee name to the @employeeList variable.
- CHAR(10) returns the line feed character.
- At last we need to print the employee list.
Statement to executes uspEmployeeList stored procedure:
EXEC uspEmployeeList 'M'
Partial Output:
Creating output parameter:
ALTER PROCEDURE uspEmployeeList(@gender VARCHAR, @employeeCount INT OUTPUT)
AS
BEGIN
SELECT
First_Name,
salary
FROM
dbo.EmployeeDb
WHERE
Gender=@gender
SELECT @employeeCount =@@ROWCOUNT
END
Syntax Description:
- Output parameter named @employeeCount is created to store the number of employee:
- After the SELECT statement, number of rows returned by the query @@ROWCOUNT to the @employeeCount parameter is assigned.
- uspEmployeeList stored procedure is compiled and saved in the database catalog.
Output(After Execution):
Commands completed successfully.
Calling stored procedures with output patameters:
After creating output parameter it can be called as:
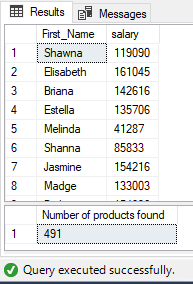
DECLARE @count INT;
EXEC uspEmployeeList
@gender = 'F',
@employeeCount = @count OUTPUT;
SELECT @count AS 'Number of products found';
Partial Output:
For SQL Server Stored Procedure: Part-2, Click here.